Digital Twin Use Cases for Performance Benchmarking and Capacity Planning
Digital twins model physical assets and processes in software to enable measurable improvements in performance benchmarking and capacity planning. This overview highlights practical applications across automation, procurement, supplychain, maintenance, IoT, sustainability, logistics, operations, compliance, analytics, outsourcing, and training.
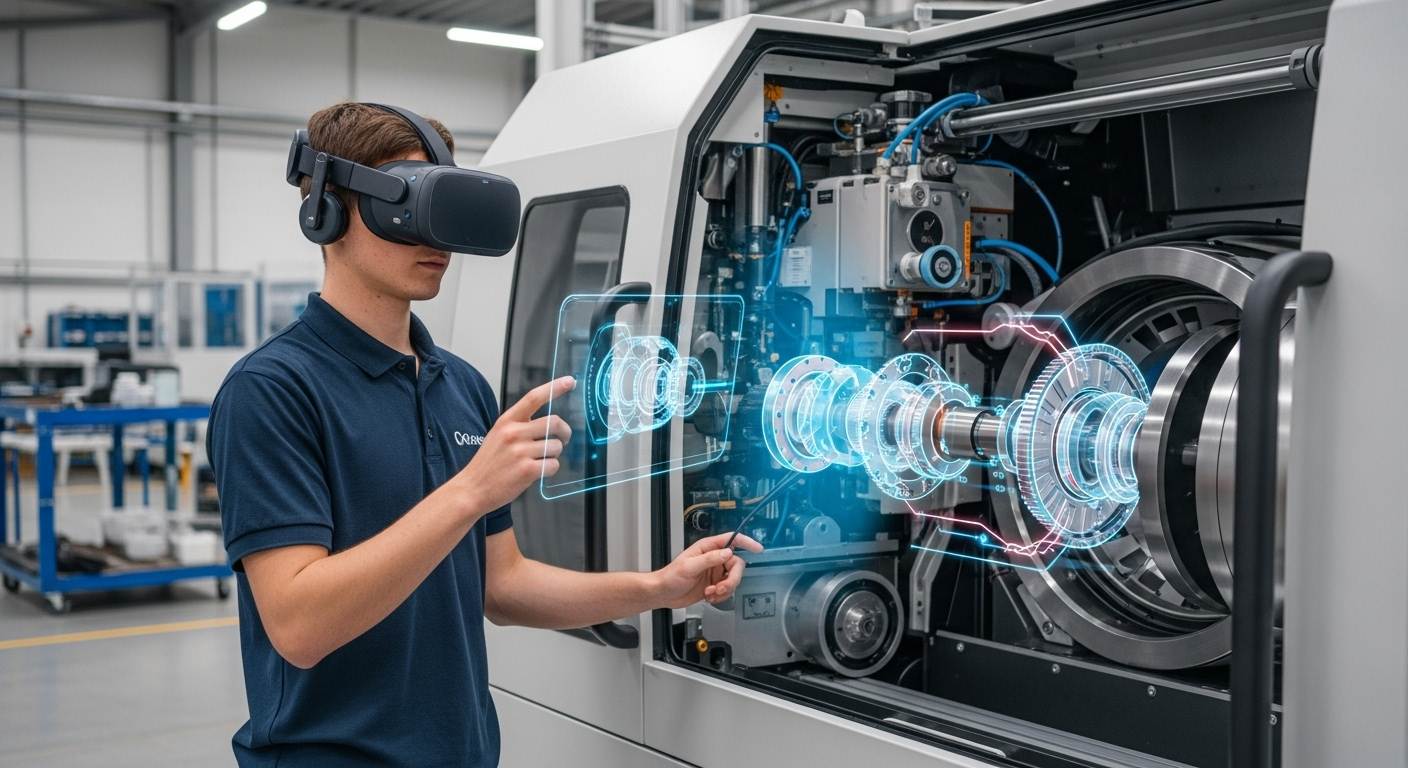

Digital twins create virtual replicas of equipment, lines, facilities, or entire supply networks to run controlled experiments without disrupting operations. By combining real-time IoT data with historical records and simulation models, organizations can benchmark performance, forecast capacity needs, and test process changes before committing resources. Practical deployment couples analytics with domain knowledge to address operational bottlenecks, improve maintenance scheduling, and align procurement and logistics with demand variability.
How does IoT enable analytics and automation?
IoT sensors feed digital twins with live telemetry—temperature, vibration, throughput, or energy use—allowing analytics engines to detect deviations from expected performance. Automated rule sets and machine learning models running on the twin can trigger alerts or closed-loop control actions in real time, improving consistency and reducing manual intervention. That integration supports process automation that is informed by both current conditions and predictive scenarios, enabling safer and faster decision cycles.
Many teams use the analytics outputs to build key performance indicators (KPIs) for benchmarking. By running side-by-side simulations using the same input data, stakeholders can compare configurations, control logic, or staffing levels and choose options that meet throughput and quality targets while minimizing risk.
How do digital twins support supplychain and logistics?
Digital twins extend beyond single assets to model flows across warehouses, transport modes, and distribution networks. Simulating logistics routes and inventory policies lets planners estimate lead times, optimize reorder points, and visualize where capacity constraints might emerge. Coupling these twins with procurement timelines and supplier performance data helps identify upstream risks and enables contingency planning without overstocking.
Scenario modeling can reveal trade-offs between expedited shipping costs and potential stockouts, guiding more resilient supplychain decisions. That supports a data-driven approach to balancing cost, service levels, and sustainability goals.
Can digital twins inform procurement and outsourcing decisions?
Yes. Virtual models let procurement teams test supplier changes, alternate materials, or outsourced processes virtually. By simulating variations in part quality, delivery reliability, or production yield, organizations can quantify the performance impact of different sourcing strategies before contracts are signed. This reduces uncertainty when considering outsourcing or switching vendors, and strengthens negotiation positions with objective metrics.
Digital twin analyses can also feed supplier scorecards and compliance checks, ensuring procurement choices align with long-term capacity and sustainability objectives.
How do they improve maintenance and operations?
Predictive maintenance is a common use case: digital twins synthesize equipment condition monitoring with degradation models to forecast failures and recommend interventions. This moves maintenance from calendar-based routines to condition-based actions that reduce downtime and spare-parts inventory. Operations teams benefit from clearer windows for repairs and better resource allocation, improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Operational simulations also allow for testing shift patterns, line sequencing, or layout changes to see how they affect throughput and worker workload, informing staffing and training plans.
What role do they play in compliance and sustainability?
Digital twins can track emissions, energy consumption, waste streams, and process deviations to support regulatory compliance and sustainability reporting. By simulating process changes—like energy recovery systems or material substitutions—teams can estimate environmental impact and operational trade-offs. This helps prioritize investments that meet compliance requirements while contributing to net-zero or circular-economy objectives.
Pairing compliance rules with real-time analytics from the twin allows quicker identification of nonconforming conditions and structured remediation steps that protect operations and reputation.
How do training and capacity planning benefit?
Virtual replicas provide immersive training environments where staff can practice procedures, emergency responses, or new workflows without risking production. For capacity planning, twins enable stress-testing of lines and facilities to quantify throughput limits under various demand scenarios. Planners can model peak-season surges, equipment outages, or supplier delays to determine where capacity expansions, overtime, or temporary outsourcing would be most effective.
These capabilities reduce the uncertainty of scaling decisions and improve alignment between operations, procurement, and finance, so capacity investments are evidence-based and less likely to be over- or under-provisioned.
Digital twins are not a silver bullet, but they are a versatile tool for measuring performance and planning capacity with greater confidence. Successful programs combine accurate IoT data, robust analytics, clear governance around compliance and procurement inputs, and user training so teams can interpret simulation results. When integrated into continuous improvement cycles across maintenance, logistics, and operations, digital twins help organizations move from reactive responses to proactive, data-driven planning and sustainable operations.